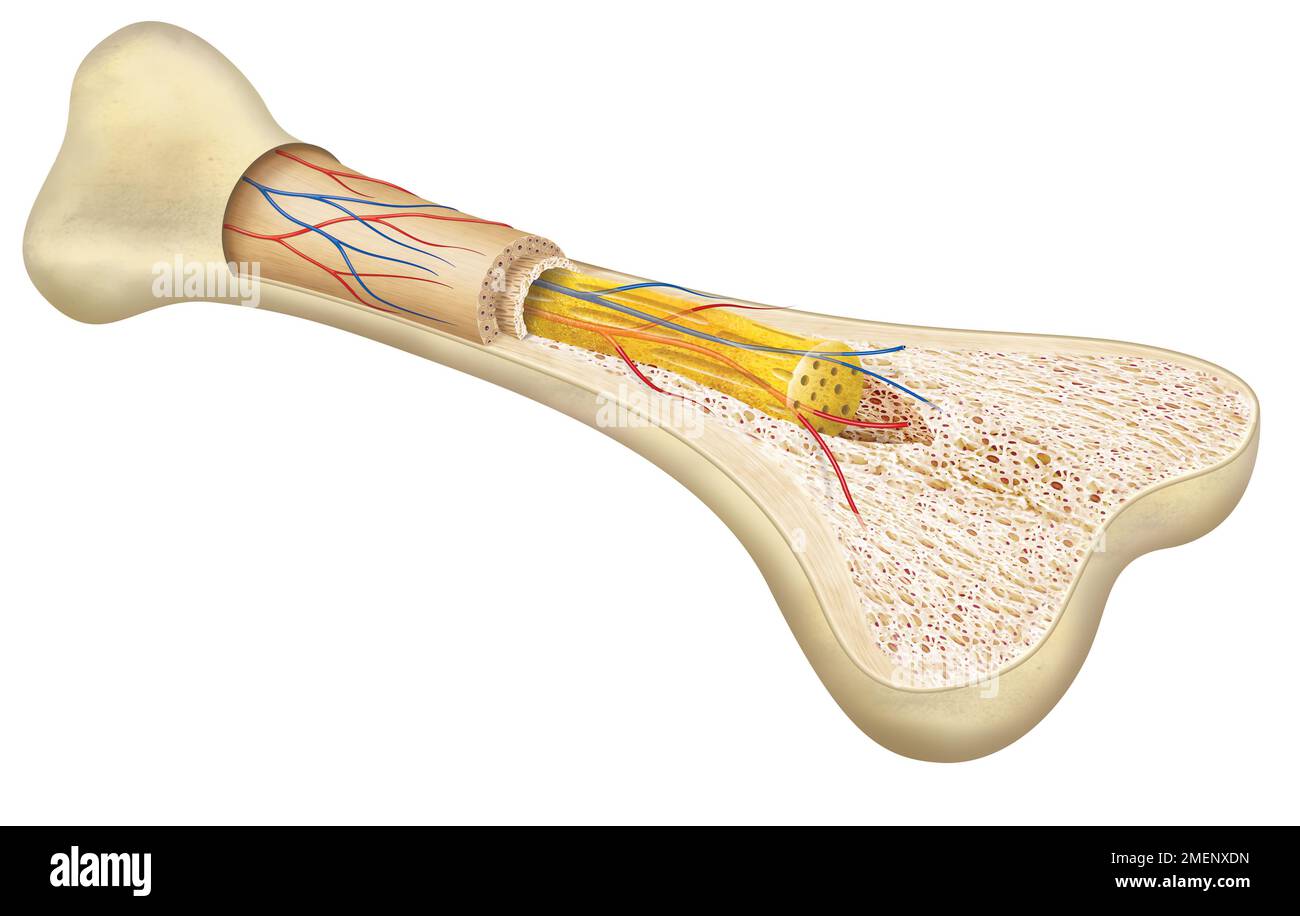
Crosssection of bone Stock Photo Alamy
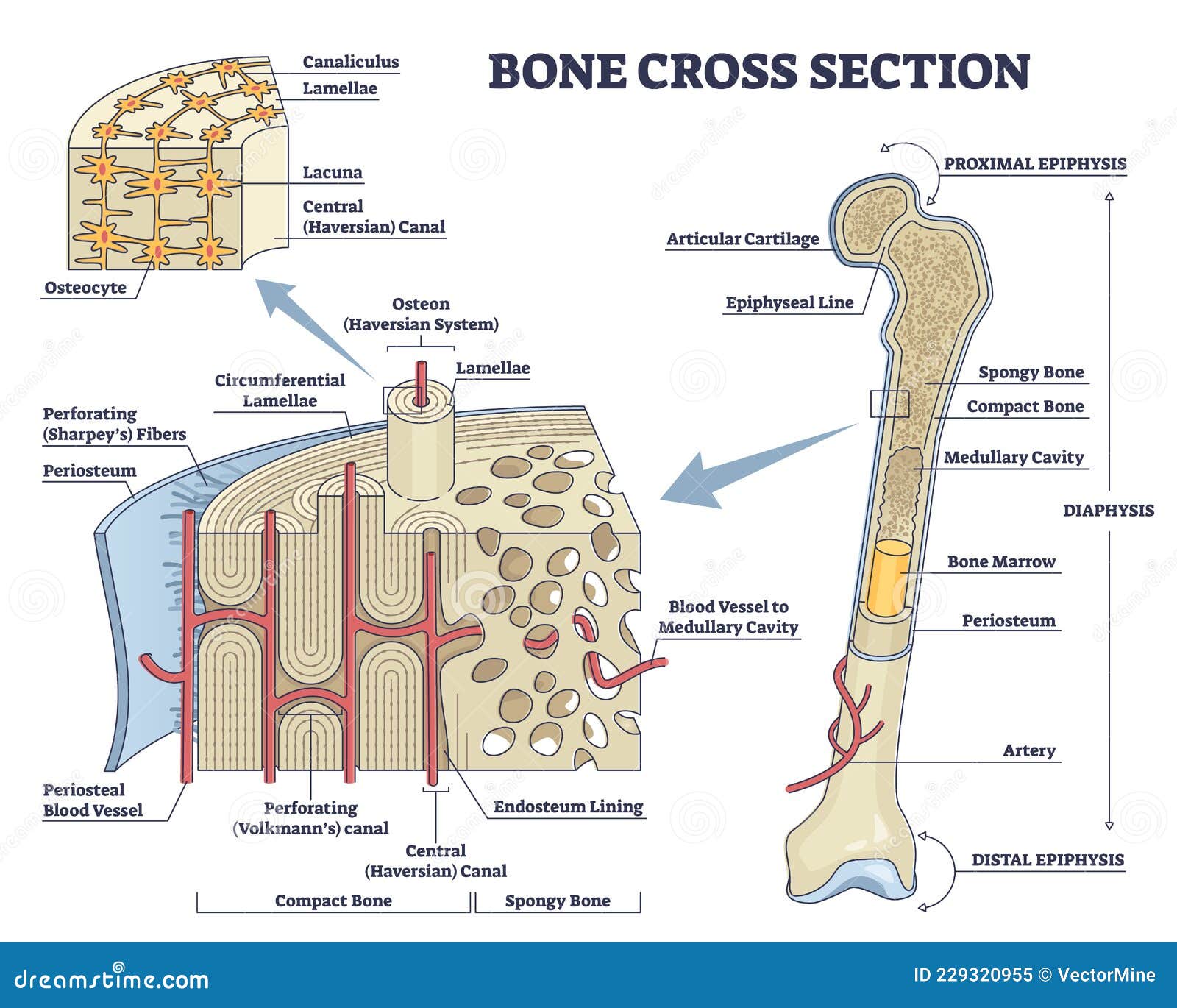
Surrounding the external surface of all bones is a layer of connective tissue termed the periosteum. In addition, lining the marrow cavity of long bones is another, considerably thinner layer of connective tissue, the endosteum. The periosteum is divided into two layers: an outer fibrous layer and an inner osteogenic layer.

Bone Cross Section Histology anatomy gross anatomy physiology cells cytology cell
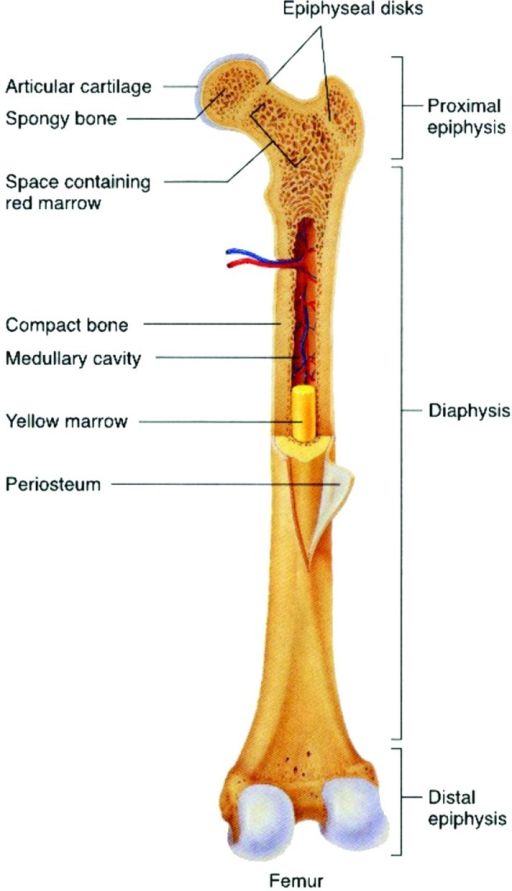
Gross Anatomy of Bone Figure 1. Anatomy of a Long Bone. A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone (Figure 1). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis.

What are the major functions of bone tissue? Britannica
Your brain is another organ that needs a lot of protection. The thick bone layer of your skull protects your brain. For this purpose, being "thick-headed" is a very good thing. Movement: Many of your bones fit together like the pieces of a puzzle. Each bone has a very specific shape which often matches up with neighboring bones.
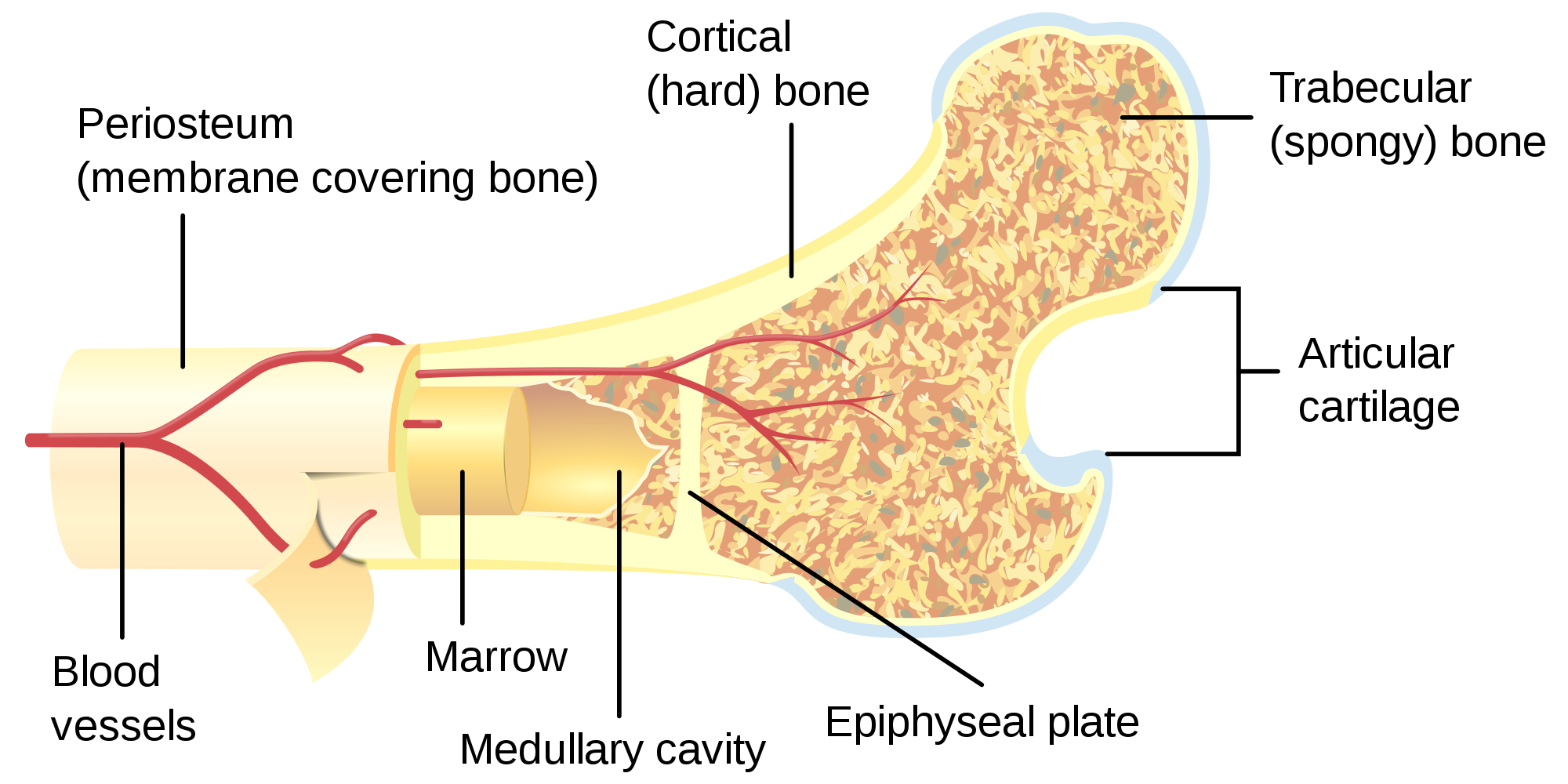
11.4 Structure of Bone Human Biology
Gross Anatomy of Bone The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( Figure 6.7 ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.

Crosssection of human bone morphology [19]. Download Scientific Diagram
The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone. Figure 6.4.1 6.4. 1: \ Anatomy of a Long Bone A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone.
"Bone Cross Section" for Radius Digital Science on Behance
Interactive Guide to the Skeletal System | Innerbody The Skeletal System Explore the skeletal system with our interactive 3D anatomy models. Learn about the bones, joints, and skeletal anatomy of the human body. By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: Jul 29, 2020 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom Anatomy Explorer HEAD AND NECK CHEST AND UPPER BACK

Bone cross section vector illustration diagram Human body science, Human anatomy and
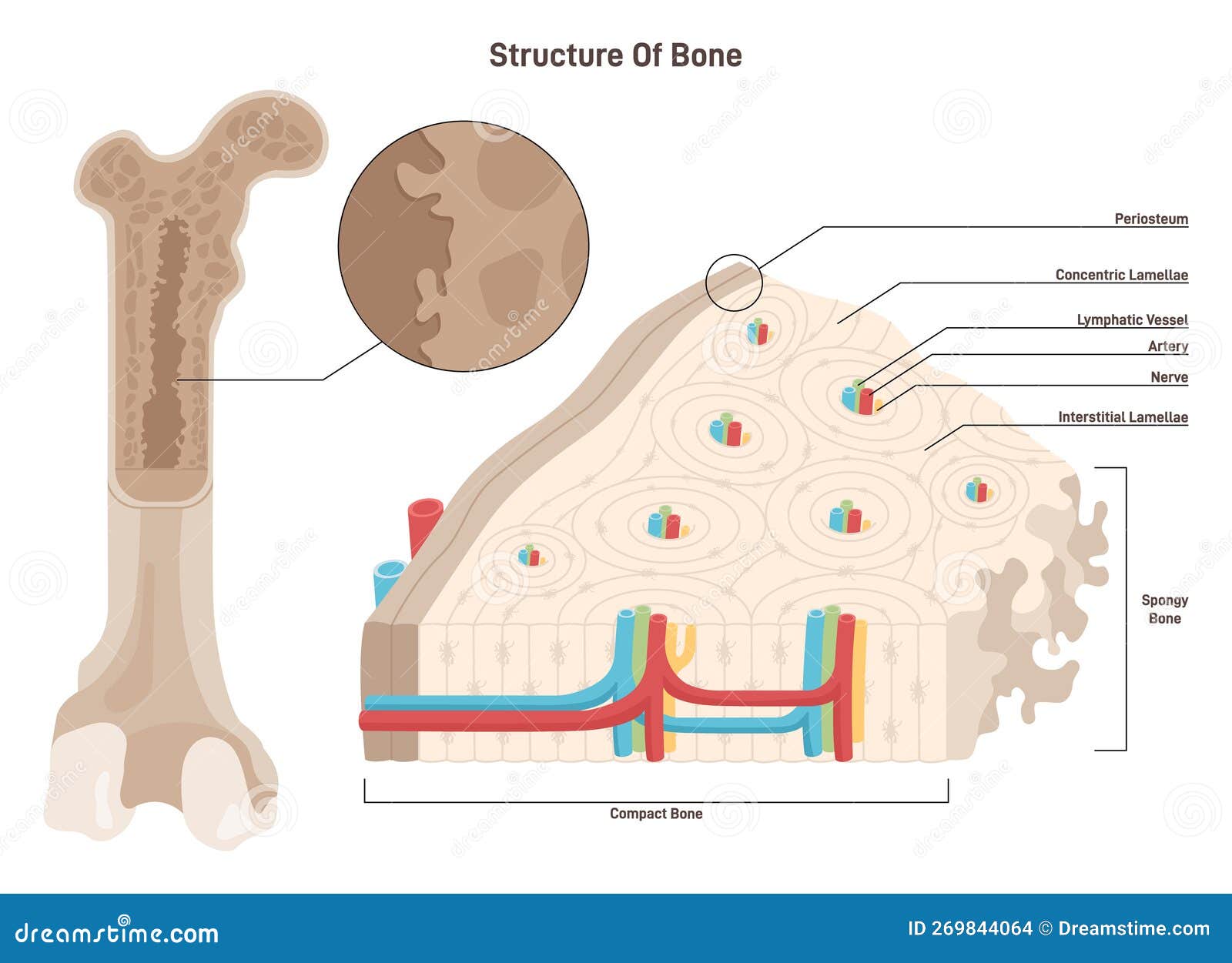
Within a cortical bone shaft, shown in cross-section (Panel A) are osteons surrounded by interstitial bone and many osteocytic lacunae distributed around the central haversian canal (Panel B.

Bone Structure · Anatomy and Physiology
6.3 Bone Structure Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the microscopic and gross anatomical structures of bones Identify the gross anatomical features of a bone Describe the histology of bone tissue, including the function of bone cells and matrix Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone
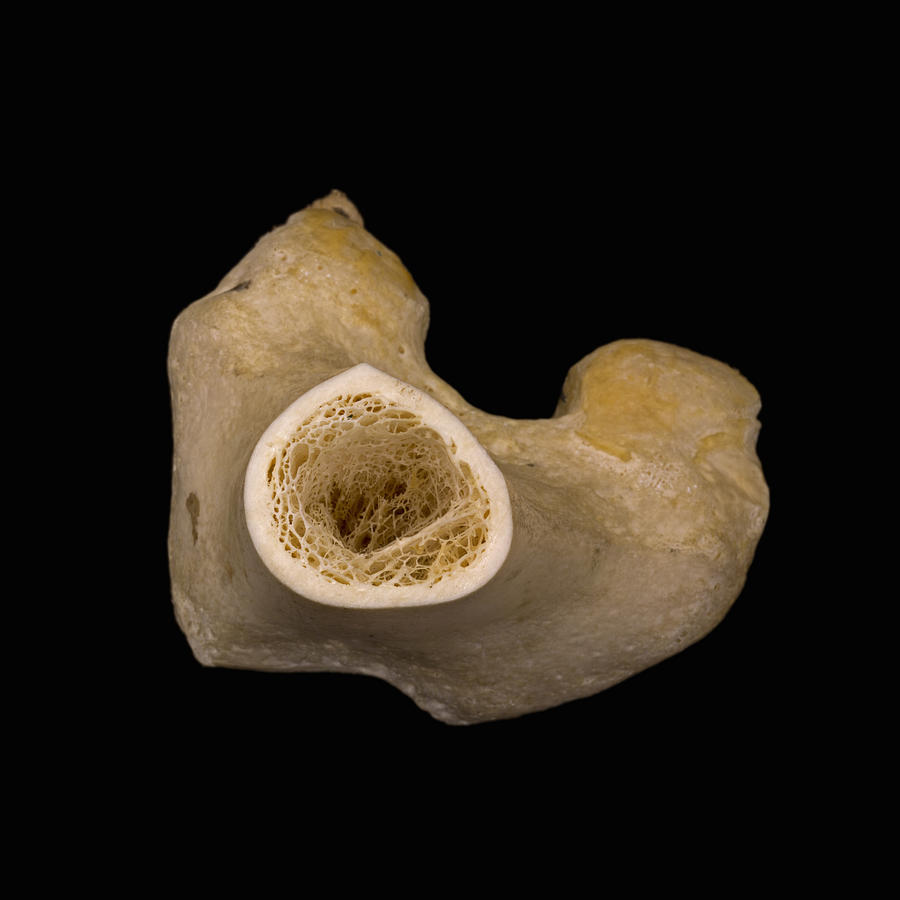
Bone Cross Section, Lm Photograph by Science Stock Photography
If you cut a cross-section through a bone, you would first come across a thin layer of dense connective tissue. This is known as the Periosteum. It consists of two layers; an outer 'fibrous layer' containing mainly fibroblasts, and an inner 'cambium layer' containing progenitor cells.

Cross Section Of A Bone Bone Cross Section Diagram Postcard / The compact bone is
More importantly, the cross sections were "easier to read" and they "better define the outlines and limits to better understand the MRI". Stated more succinctly, cross-sections are essential. Vertebral body of L3 (MRI image) So far, it appears that cross-sections tick the boxes of preference and understanding.

"Bone Cross Section" for Radius Digital Science on Behance
Gross Anatomy of Bone The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( [link] ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
Long Bone Cross Section Labeled Cataleya Tait
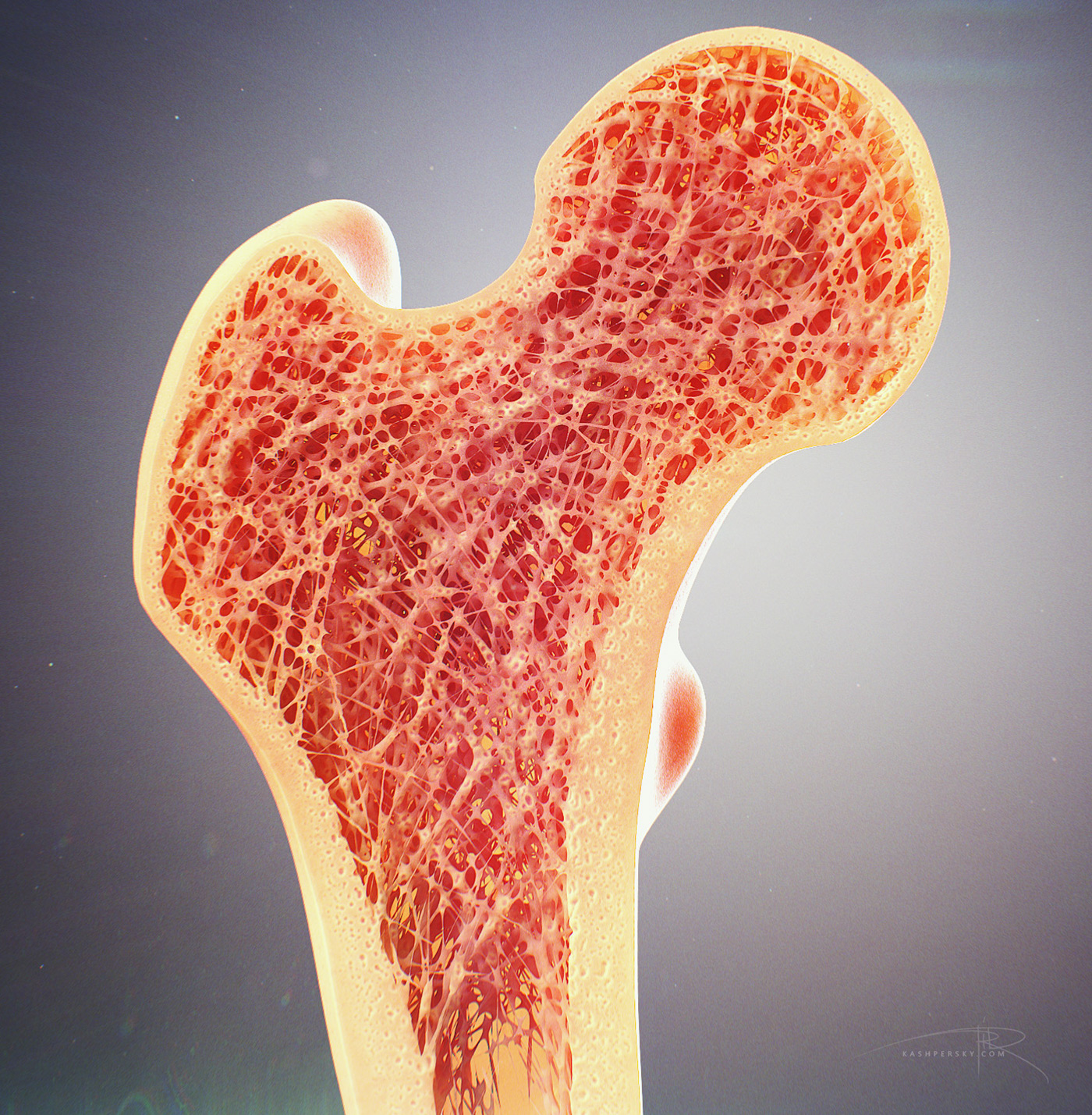
Bone tissue is a mineralized tissue of two types: compact bone (cortical) and spongy bone (trabecular or cancellous). Above: A cross section of bone tissue shows the outer layers are composed of compact bone and the inner layers are composed of spongy bone.
Bone Cross Section. Anatomical Detailed Structure of Bone Tissue Stock Vector Illustration of
1/7 Synonyms: Dorsal thalamus, Thalamencephalon , show more. Cross-sections are two-dimensional, axial views of gross anatomical structures seen in transverse planes. They are obtained by taking imaginary slices perpendicular to the main axis of organs, vessels, nerves, bones, soft tissue, or even the entire human body.

Bone Cross Section 3D model CGTrader
There are three distinct types of fibula shapes when viewed as a cross-section along the shaft: triangular, quadrilateral, and irregular. Each fibula can contain more than one type of cross-section shape, and the combinations differ between males and females. The fibula is the most slender long bone in the body as a ratio of width to length.
Bone Cross Section and Isolated Anatomical Detailed Structure Outline Diagram Stock Vector
In a cross-section, the fibers of lamellar bone can be seen to run in opposite directions in alternating layers, much like in plywood, assisting in the bone's ability to resist torsion forces. When the same lamellar bone is loosely arranged, it is referred to as trabecular bone. Trabecular bone gets its name because of the spongy pattern it.

Cross section view of a human femur bone showing trabecula Stock Photo Alamy
INTRODUCTION O STEOPOROSIS IS defined by abnormalities in both the amount of bone and the architectural arrangement of bone tissue, leading to decreased skeletal strength and increased fragility and fracture risk. 1 The role of low bone density in fracture risk in various skeletal regions is well established.